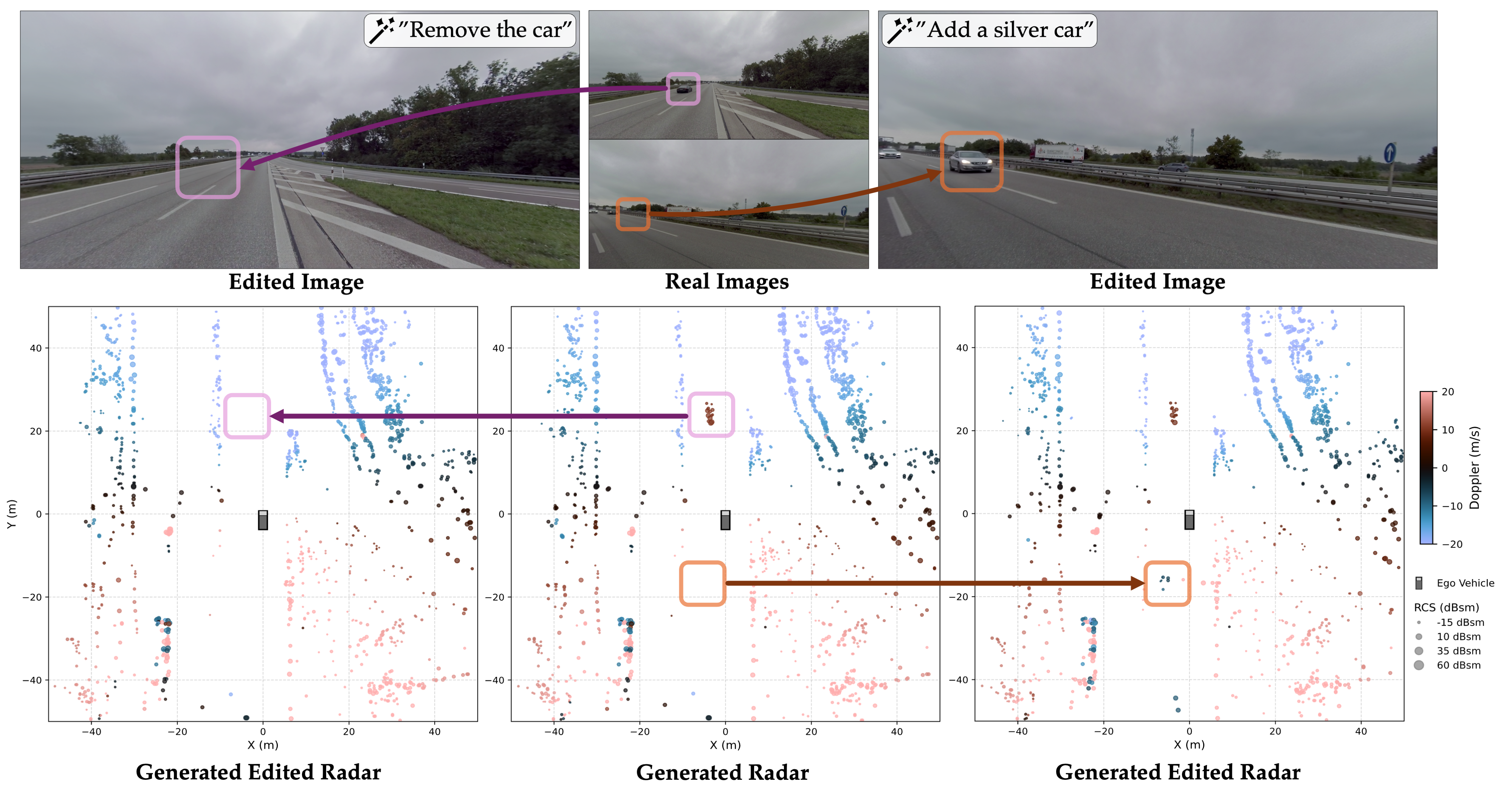
We present RadarGen, a diffusion model for synthesizing realistic automotive
radar point clouds from multi-view camera imagery.
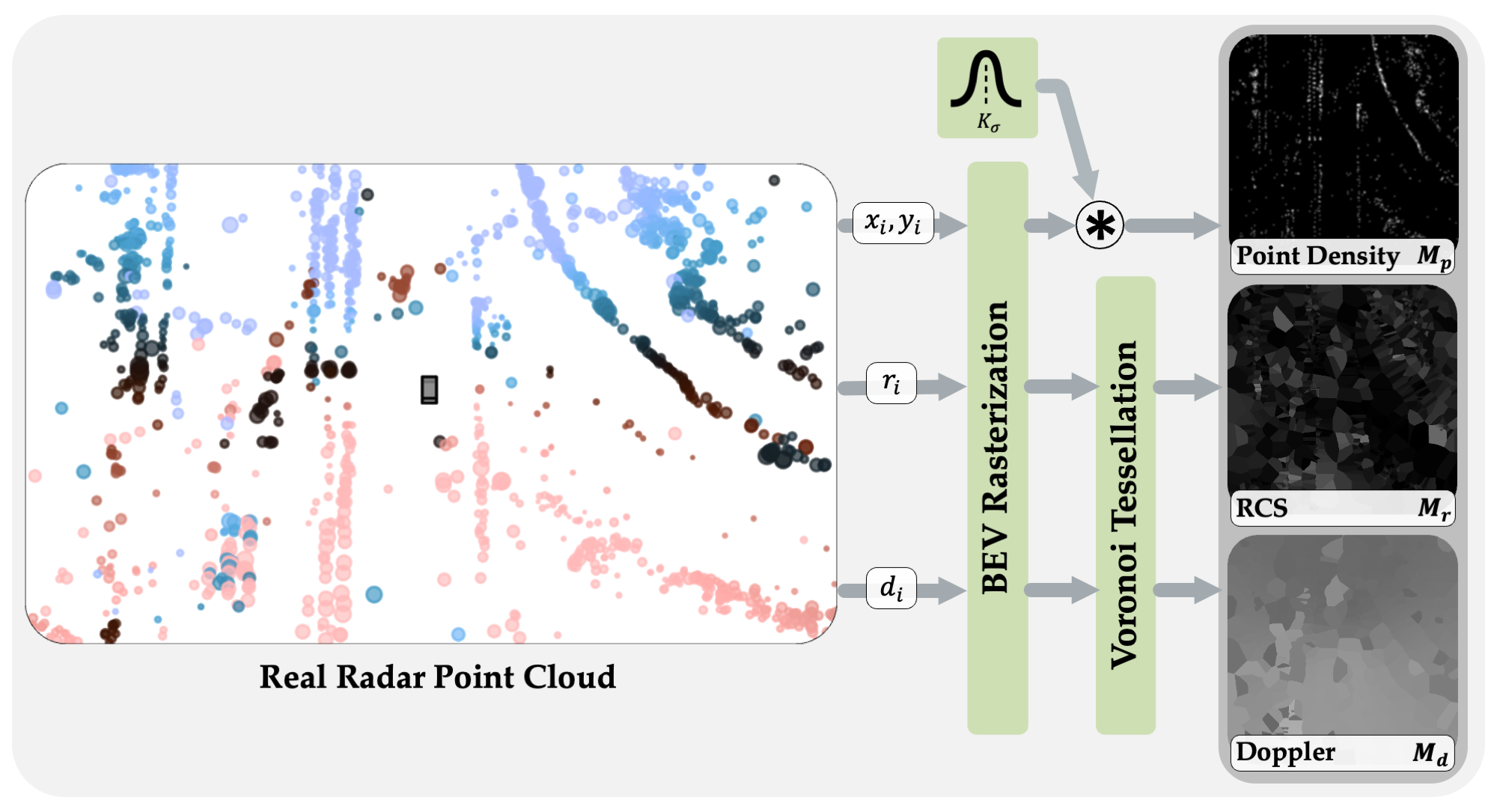
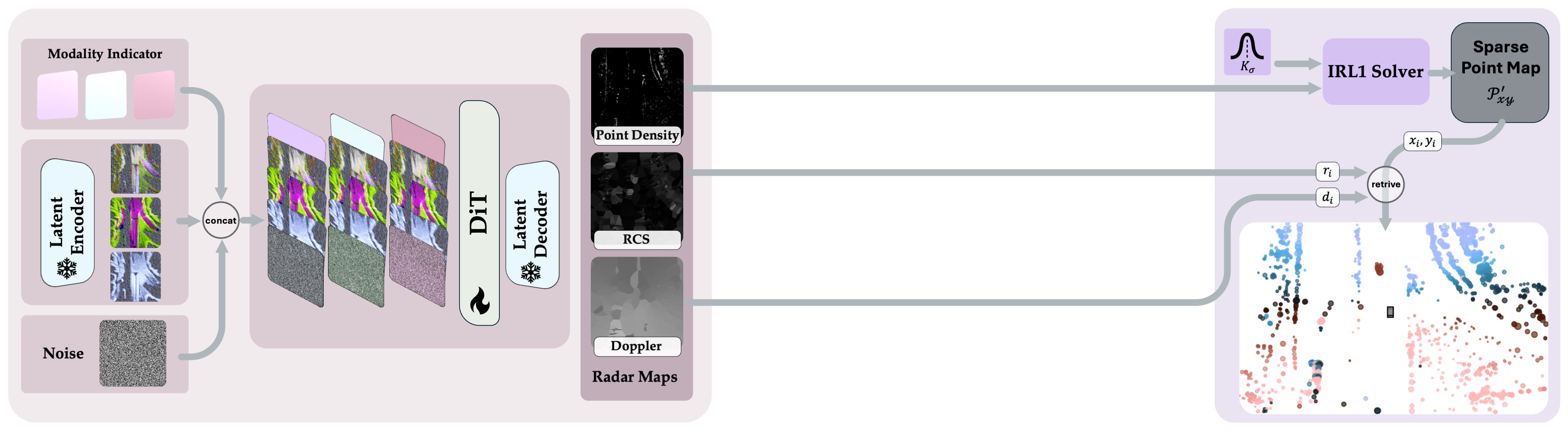
RadarGen adapts efficient image-latent diffusion to the radar domain by
representing radar measurements in bird’s-eye-view form that encodes spatial structure together with
radar cross
section (RCS) and Doppler attributes.
A lightweight recovery step reconstructs point clouds from the generated maps.
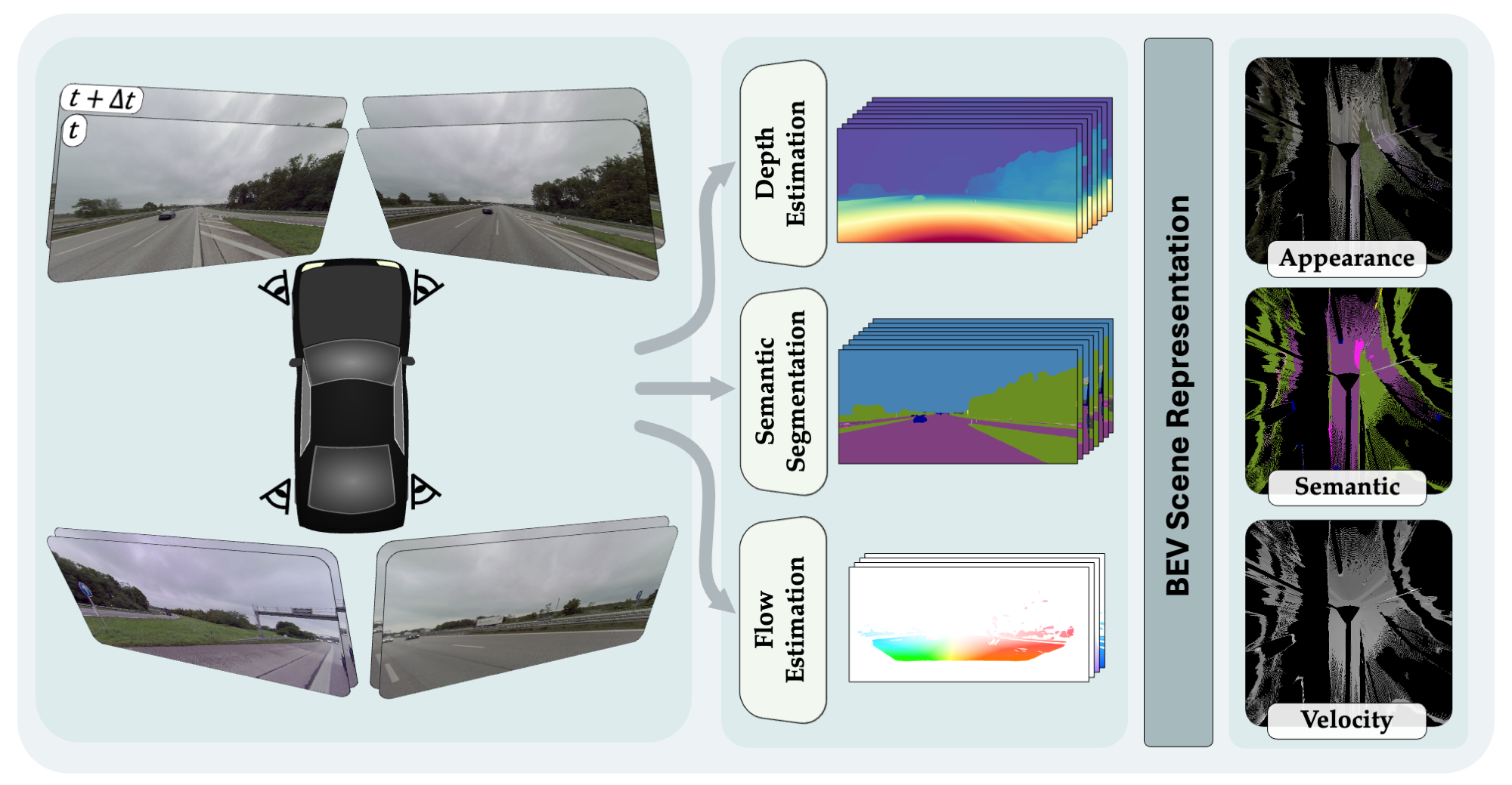
To better align generation with the visual scene, RadarGen incorporates
BEV-aligned depth, semantic, and motion cues extracted from pretrained foundation models, which
guide the stochastic generation
process toward physically plausible radar patterns.
Conditioning on images makes the approach broadly compatible, in principle, with existing visual
datasets and simulation frameworks, offering a scalable direction for multimodal generative
simulation.
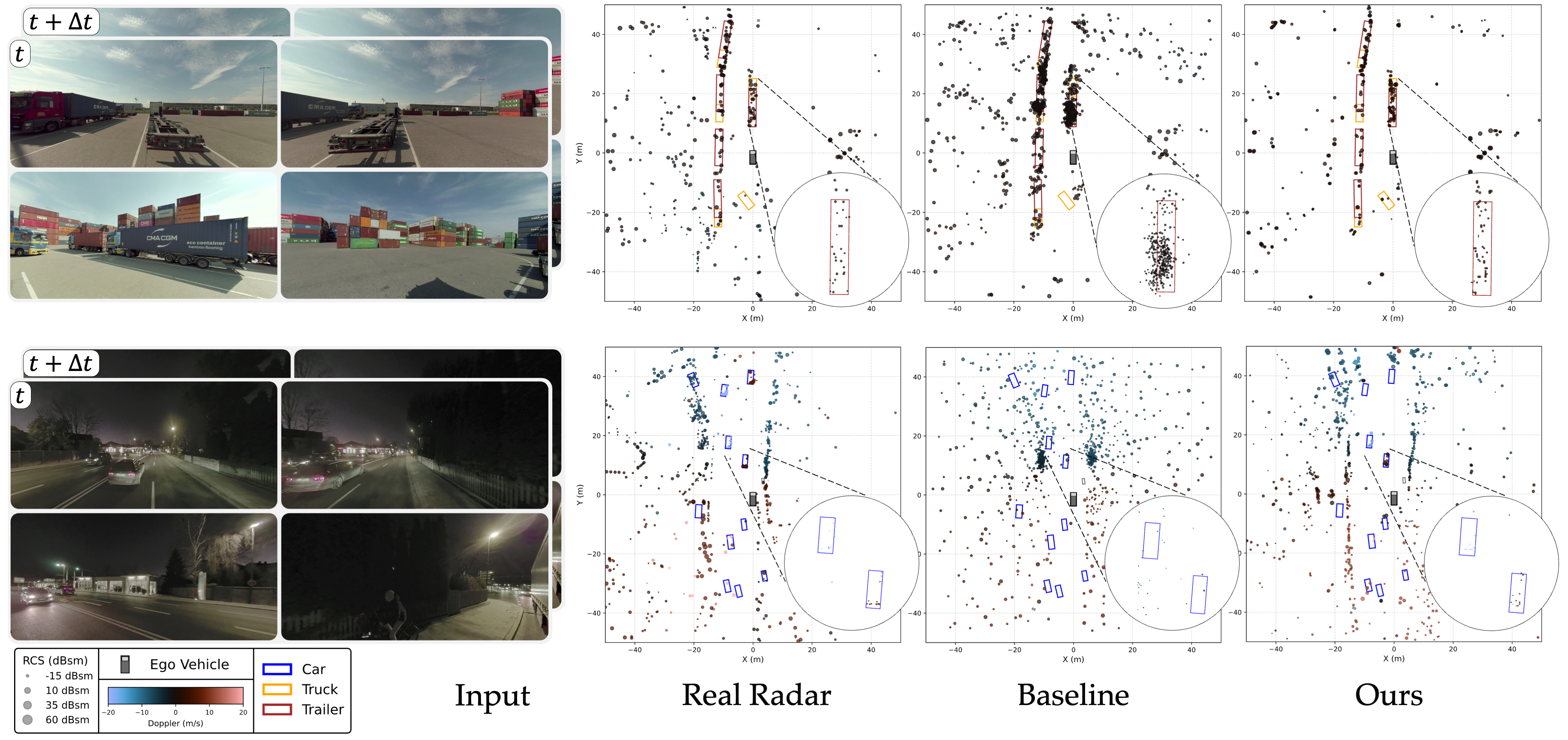
Evaluations on large-scale driving data show that RadarGen captures
characteristic radar measurement
distributions and reduces the gap to perception models trained on real data, marking a step toward
unified generative simulation across sensing modalities.